Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a leading cause of vision loss in people over the age of 50. It affects the macula, the part of the eye responsible for sharp, central vision needed for tasks like reading and driving. While there is no cure for AMD, there are several preventive measures that can help reduce the risk of developing the condition or slow its progression. Understanding these measures and their impact can empower individuals to take proactive steps towards preserving their vision.
Types of AMD
There are two types of AMD: dry and wet. Dry AMD is more common and progresses slowly, causing gradual vision loss. Wet AMD is less common but more severe, leading to rapid vision loss due to abnormal blood vessel growth under the retina. Early detection and intervention are crucial in managing both types.
Risk Factors
Several risk factors are associated with AMD, including age, family history, smoking, high blood pressure, and obesity. While some factors, like age and genetics, cannot be controlled, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of developing AMD or slow its progression.
Dietary Measures
Nutrient-Rich Foods
Consuming a diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can help protect the eyes from AMD. Foods high in vitamins C and E, zinc, lutein, and zeaxanthin are particularly beneficial. These nutrients are found in leafy green vegetables, fruits, nuts, and fish. Including these foods in your diet can support eye health and reduce the risk of AMD.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, have anti-inflammatory properties that may help protect against AMD. Including these fish in your diet at least twice a week can contribute to better eye health.
Supplements
In some cases, dietary supplements can provide additional support. The Age-Related Eye Disease Study (AREDS) has shown that high-dose antioxidant and zinc supplements can reduce the risk of advanced AMD. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen to ensure it is appropriate for your individual needs.
Lifestyle Changes
Quit Smoking
Smoking is a significant risk factor for AMD. It doubles the risk of developing the condition and accelerates its progression. Quitting smoking is one of the most effective preventive measures you can take to protect your vision. There are various resources and support systems available to help you quit smoking and maintain a smoke-free lifestyle.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Obesity is linked to an increased risk of AMD. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce this risk. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week to support overall health and eye health.
Manage Blood Pressure and Cholesterol
High blood pressure and high cholesterol levels can contribute to the development and progression of AMD. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider, along with lifestyle changes and medications if necessary, can help manage these conditions and reduce the risk of AMD.
Eye Protection
Wear Sunglasses
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light can damage the eyes and increase the risk of AMD. Wearing sunglasses that block 100% of UV rays can help protect your eyes. Additionally, wearing a wide-brimmed hat can provide extra protection from the sun.
Use Protective Eyewear
If you engage in activities that pose a risk of eye injury, such as sports or working with hazardous materials, wearing protective eyewear is essential. Preventing eye injuries can help maintain overall eye health and reduce the risk of AMD.
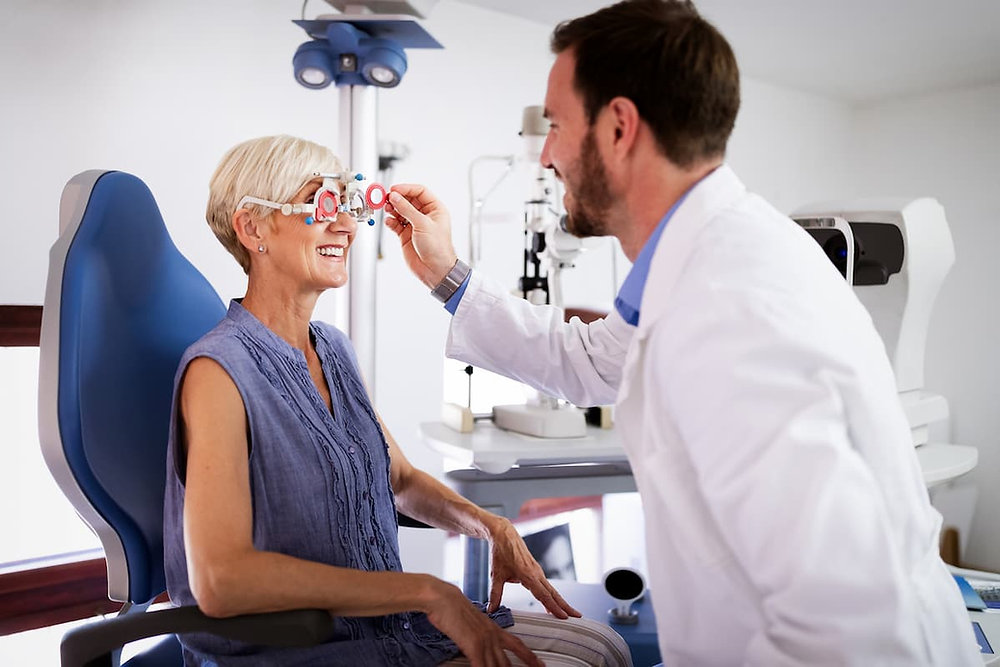
Regular Eye Exams
Early Detection
Regular comprehensive eye exams are crucial for detecting early signs of AMD. Early detection allows for timely intervention and management, which can slow the progression of the disease. Eye exams can also identify other eye conditions that may contribute to vision loss.
Monitoring Progression
If you have already been diagnosed with AMD, regular eye exams are essential for monitoring the progression of the disease. Your eye care professional can adjust your treatment plan as needed to ensure optimal management of your condition.
Age-Related Macular Degeneration Treatment Options
Current Treatments
While there is no cure for AMD, several treatment options can help manage the condition and slow its progression. For dry AMD, the focus is on lifestyle changes and nutritional supplements. Wet AMD treatment includes anti-VEGF injections, and less commonly photodynamic therapy to prevent abnormal blood vessel growth and preserve vision.
Research and Advancements
Ongoing research is continually advancing the field of age-related macular degeneration treatment. Clinical trials and studies are exploring new therapies and interventions that may provide better outcomes for individuals with AMD. Staying informed about the latest advancements can help you and your healthcare provider make informed decisions about your treatment options.
Conclusion
Preventive measures play a crucial role in reducing the risk of age-related macular degeneration and slowing its progression. By adopting a healthy diet, making lifestyle changes, protecting your eyes, and scheduling regular eye exams, you can take proactive steps towards preserving your vision.